What is the Most Common Cause of Hearing Loss in Children

Did you know that hearing loss can affect children of all ages, from infants to adolescents? As parents and caregivers, it’s essential to be aware of the most common cause of hearing loss in children and how it can impact their development and overall well-being.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the question: What is the most common cause of hearing loss in children? By understanding the answer to this question, we can take proactive steps to support children with hearing loss and ensure they receive the necessary care and intervention. Let’s dive into the discussion to learn more about this important topic.
What is Hearing Loss?
Hearing loss refers to a partial or total inability to hear sounds. It can range from mild to profound and may affect one or both ears. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent and may occur at any age, including infancy and childhood.
Common Cause of Hearing Loss in Children
1. Genetic Factors
- Genetic factors play a significant role in congenital hearing loss, which is present at birth. Inherited genetic abnormalities or syndromes, such as sensorineural hearing loss or genetic syndromes like Down syndrome, can contribute to hearing loss in children.
- Approximately 50-60% of congenital hearing loss cases have a genetic cause. Screening for genetic factors and family history of hearing loss can help identify children at risk and facilitate early intervention.
2. Complications at Birth
- Complications during pregnancy, childbirth, or shortly after birth can lead to hearing loss in children. Premature birth, low birth weight, lack of oxygen during birth (asphyxia), or infections acquired during childbirth can damage the auditory system and result in hearing loss.
- Neonatal screening programs and early detection of hearing loss in newborns are essential for identifying and addressing hearing loss resulting from birth complications.
3. Ear Infections
- Ear infections, particularly otitis media, are a common cause of acquired hearing loss in children. Chronic or recurrent ear infections can lead to fluid buildup in the middle ear, resulting in temporary or permanent hearing loss if left untreated.
- Timely diagnosis and treatment of ear infections, including appropriate antibiotic therapy and surgical intervention if necessary, can help prevent hearing loss and minimize its impact on children’s development.
4. Noise Exposure
- Prolonged exposure to loud noises, either from environmental sources or recreational activities, can damage the delicate structures of the inner ear and lead to hearing loss over time. Children exposed to loud noises without adequate hearing protection are at risk of noise-induced hearing loss.
- Educating children and parents about the importance of hearing protection and limiting exposure to loud noises can help prevent noise-induced hearing loss in children.
5. Head Trauma
- Head trauma resulting from accidents, falls, or sports injuries can cause damage to the auditory system and result in hearing loss. Traumatic brain injury or damage to the auditory nerves can impair the child’s ability to hear sounds effectively.
- Prompt medical evaluation and treatment of head injuries are essential for assessing the extent of hearing loss and implementing appropriate interventions.
6. Other Factors
- Other less common factors that can contribute to hearing loss in children include ototoxic medications, congenital abnormalities of the ear, tumors or growths in the auditory system, and certain medical conditions affecting the auditory system.
- Comprehensive medical evaluation, including hearing tests and diagnostic imaging studies, may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of hearing loss and guide treatment decisions.
Understanding the various causes of hearing loss in children is essential for early detection, intervention, and support. By recognizing the signs and risk factors associated with hearing loss, parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals can take proactive steps to address hearing loss and minimize its impact on children’s development and well-being. With early intervention and appropriate management, children with hearing loss can thrive and achieve their full potential.
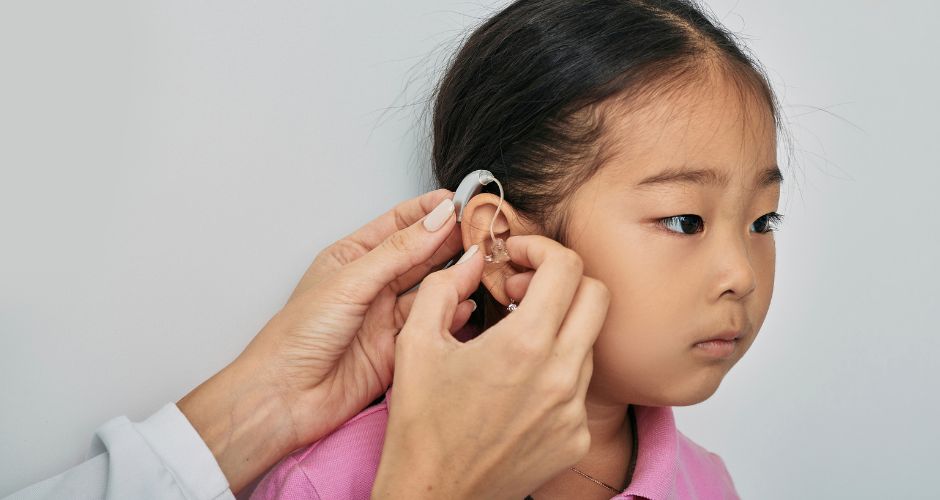
Preventing Hearing Loss in Children
Hearing loss in children can have a significant impact on their development, communication skills, and overall quality of life.
- Maintain Regular Hearing Screenings: Schedule regular hearing screenings for newborns and young children as part of routine pediatric care. Early detection of hearing loss allows for prompt intervention and support, minimizing the impact on the child’s development.
- Avoid Exposure to Loud Noise: Protect children’s ears from exposure to loud noises, including music concerts, fireworks, power tools, and recreational activities like shooting or motorcycling. Use ear protection devices such as earmuffs or earplugs in noisy environments to prevent noise-induced hearing loss.
- Monitor Ear Health: Stay vigilant for signs of ear infections, which can lead to temporary or permanent hearing loss if left untreated. Seek prompt medical attention for ear infections and follow treatment recommendations to prevent complications and preserve hearing.
- Limit Use of Headphones and Electronic Devices: Encourage safe listening habits by limiting the use of headphones and electronic devices with high volume settings. Set volume limits on devices and encourage children to take regular breaks to rest their ears.
- Practice Good Ear Hygiene: Teach children proper ear hygiene practices, such as avoiding the use of cotton swabs or other objects to clean the ears. Encourage gentle cleaning of the outer ear with a damp cloth and avoid inserting objects into the ear canal.
- Educate About Hearing Health: Educate children about the importance of protecting their hearing and practicing healthy listening habits. Teach them to recognize signs of hearing loss, such as difficulty hearing conversations or ringing in the ears, and to seek help if they experience any symptoms.
- Promote Overall Health and Wellness: Encourage a healthy lifestyle that includes balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and adequate rest. Maintaining overall health and wellness can support optimal auditory function and reduce the risk of hearing loss.
By implementing these strategies for preventing hearing loss in children, we can safeguard their auditory health and ensure they have the best possible chance for optimal hearing and communication skills. Together, let’s prioritize proactive measures to protect children’s hearing and promote lifelong auditory well-being.
Read more – 9 Best Sources of Calcium for Kids



