How to Deal with Dental Phobia or Anxiety?

Are you one to dodge dental appointments, despite knowing they’re necessary? Does the mere idea of settling into that dentist’s chair send shivers down your spine, filling you with anxiety?
Fear of the dentist’s chair is a widespread and formidable challenge that plagues countless individuals worldwide. This fear often obstructs people from seeking vital dental care, jeopardizing their oral health in the process.
Dental phobia, also known as odontophobia, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The fear and anxiety associated with dental visits can have a significant impact on oral health and overall well-being.
Causes of Dental Phobia
- Previous Traumatic Experiences: One of the most common causes of dental phobia is a negative or traumatic experience during a dental procedure. This may include experiencing pain, discomfort, or feeling out of control during past dental visits.
- Fear of Pain: Many individuals fear the possibility of experiencing pain or discomfort during dental procedures, leading to heightened anxiety and avoidance of dental appointments.
- Fear of Needles or Injections: Some people have a phobia of needles or injections, which are commonly used in dental treatments such as local anesthesia or numbing injections.
- Loss of Control: Feeling vulnerable or losing control in the dental chair can trigger anxiety in individuals with dental phobia. This fear may stem from a lack of understanding or communication with the dentist about the procedure.
- Embarrassment or Self-Consciousness: Individuals may feel embarrassed or self-conscious about the condition of their teeth or mouth, leading to anxiety and avoidance of dental care.
- Negative Media Portrayals: Negative portrayals of dentistry in media or popular culture, such as movies or television shows depicting dental procedures as painful or traumatic, can contribute to dental phobia.
- Fear of Judgment: Some individuals fear being judged or criticized by dental professionals for the condition of their teeth or oral hygiene habits, leading to avoidance of dental appointments.
- Anxiety Disorders: Individuals with pre-existing anxiety disorders or other mental health conditions may be more susceptible to developing dental phobia due to heightened levels of anxiety and stress.
Symptoms of Dental Phobia
- Intense Fear or Anxiety: Individuals with dental phobia experience overwhelming fear or anxiety at the thought of visiting the dentist or undergoing dental procedures. This fear may be disproportionate to the actual threat posed by the situation.
- Physical Symptoms: Dental phobia can manifest in physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling, rapid heartbeat (palpitations), dizziness, or nausea when faced with dental appointments or even the thought of visiting the dentist.
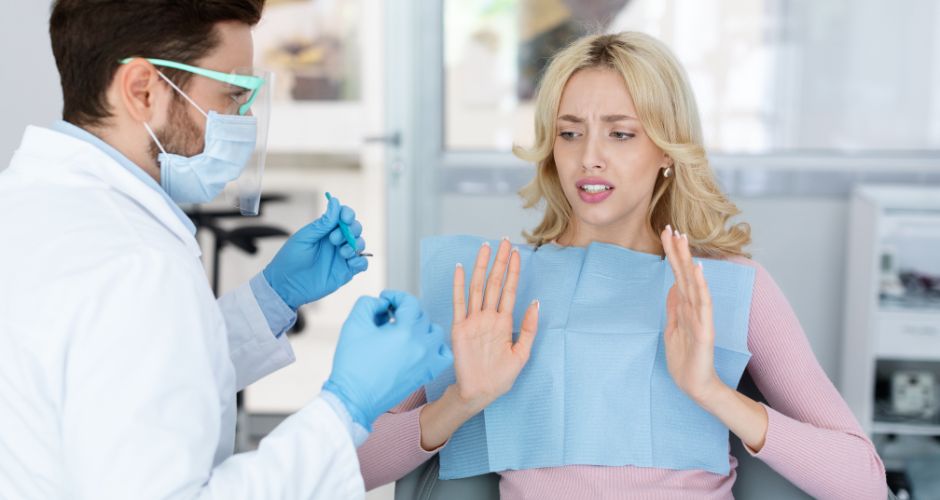

- Difficulty Sleeping or Concentrating: Dental-related worries and anxiety can interfere with sleep patterns and concentration levels, leading to difficulty sleeping or focusing on daily tasks.
- Avoidance Behavior: People with dental phobia may avoid scheduling dental appointments altogether or canceling appointments at the last minute due to overwhelming anxiety and fear. This avoidance behavior can lead to neglect of oral health and worsening dental problems over time.
- Panic Attacks: In severe cases, dental phobia can trigger panic attacks characterized by sudden and intense feelings of fear or dread, accompanied by physical symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or feelings of impending doom.
- Psychological Distress: Dental phobia can cause significant psychological distress and impairment in daily functioning, affecting interpersonal relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
How to Treat Dental Phobia
- Open Communication: Discuss your fears and concerns with your dentist openly and honestly. A compassionate and understanding dentist can work with you to alleviate anxiety and create a comfortable treatment plan.
- Gradual Exposure: Gradually expose yourself to dental environments and procedures to desensitize yourself to triggers. Start with simple visits, such as consultations or cleanings, before progressing to more complex procedures.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or visualization to reduce stress and anxiety before and during dental appointments.
- Sedation Dentistry: Consider sedation options such as nitrous oxide (laughing gas), oral sedatives, or intravenous (IV) sedation for more complex procedures or severe anxiety. These methods can help you relax and feel more comfortable during dental treatment.
- Behavioral Therapy: Seek support from a mental health professional who specializes in treating phobias or anxiety disorders. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and exposure therapy can be effective in addressing underlying fears and changing negative thought patterns associated with dental phobia.
- Medication: In some cases, anti-anxiety medications or sedatives may be prescribed to help manage severe dental phobia. These medications can be taken before dental appointments to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
- Dental Desensitization Programs: Some dental practices offer desensitization programs specifically designed to help individuals overcome dental phobia. These programs gradually expose patients to dental procedures in a controlled and supportive environment, allowing them to build confidence and reduce anxiety over time.
- Supportive Dental Team: Choose a dental team that is experienced in working with anxious patients and provides a supportive and non-judgmental environment. Building a trusting relationship with your dentist and dental staff can help alleviate anxiety and make dental visits more comfortable.
By implementing these strategies and seeking support from dental professionals and mental health experts, individuals can effectively manage and overcome dental phobia, allowing them to receive necessary dental care and maintain optimal oral health.
Recommended – Why Do I Have a Hole in My Gum